How to operate a drone? It’s more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and prioritizing safety. This guide delves into the essential steps for safely and effectively piloting a drone, from pre-flight checks and navigation to capturing stunning aerial footage and handling emergencies. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies.
From understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different flight modes to mastering high-quality aerial photography and video, we will equip you with the knowledge to become a proficient drone operator. We’ll also explore crucial aspects such as battery management, maintenance, and emergency procedures, ensuring a smooth and safe flying experience.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource to help you get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from controlling the drone’s movements to understanding battery life and safety procedures, ensuring a smooth and safe flying experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before taking flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring both the safety of your drone and those around you. This involves a systematic inspection of various components and a careful consideration of environmental factors and regulations. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection

A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is paramount for safe drone operation. The following table Artikels key areas to check:
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or imbalance. | Replace damaged propellers. | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. |
| Battery | Check battery level and health. | Charge battery if necessary; replace if damaged or showing signs of wear. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clean lens if necessary. | Check SD card for sufficient space. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | Tighten screws if loose. | Ensure gimbal is properly calibrated. |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage or loose parts. | Tighten any loose screws or bolts. | Check for any signs of wear and tear. |
| GPS and Compass | Ensure GPS signal is strong and compass is calibrated. | Recalibrate if necessary. | Allow sufficient time for GPS acquisition. |
| Remote Controller | Check battery level and ensure proper connection with the drone. | Charge remote controller battery if needed. | Verify all controls are responsive. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Understanding and adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions is non-negotiable. Flying without proper authorization can result in hefty fines or legal consequences. Always check with the relevant aviation authorities before operating your drone.
Safety Precautions
Prioritizing safety is paramount. The following precautions should always be observed:
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports, helipads, or other restricted airspace.
- Avoid flying in crowded areas or near people.
- Never fly your drone in adverse weather conditions (strong winds, rain, snow).
- Be mindful of other aircraft and obstacles.
- Always have a backup plan in case of malfunctions.
- Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures.
Safe Drone Operation in Various Weather Conditions

A flowchart is a useful tool for making informed decisions regarding safe drone operation in different weather scenarios. The decision-making process should consider factors like wind speed, visibility, and precipitation. A simple flowchart would start with assessing the weather conditions, then proceed to a decision point regarding flight safety based on pre-defined thresholds. If conditions are unsafe, the flowchart would lead to a “Do Not Fly” decision, otherwise to “Proceed with Flight,” with additional safety checks incorporated before flight commencement.
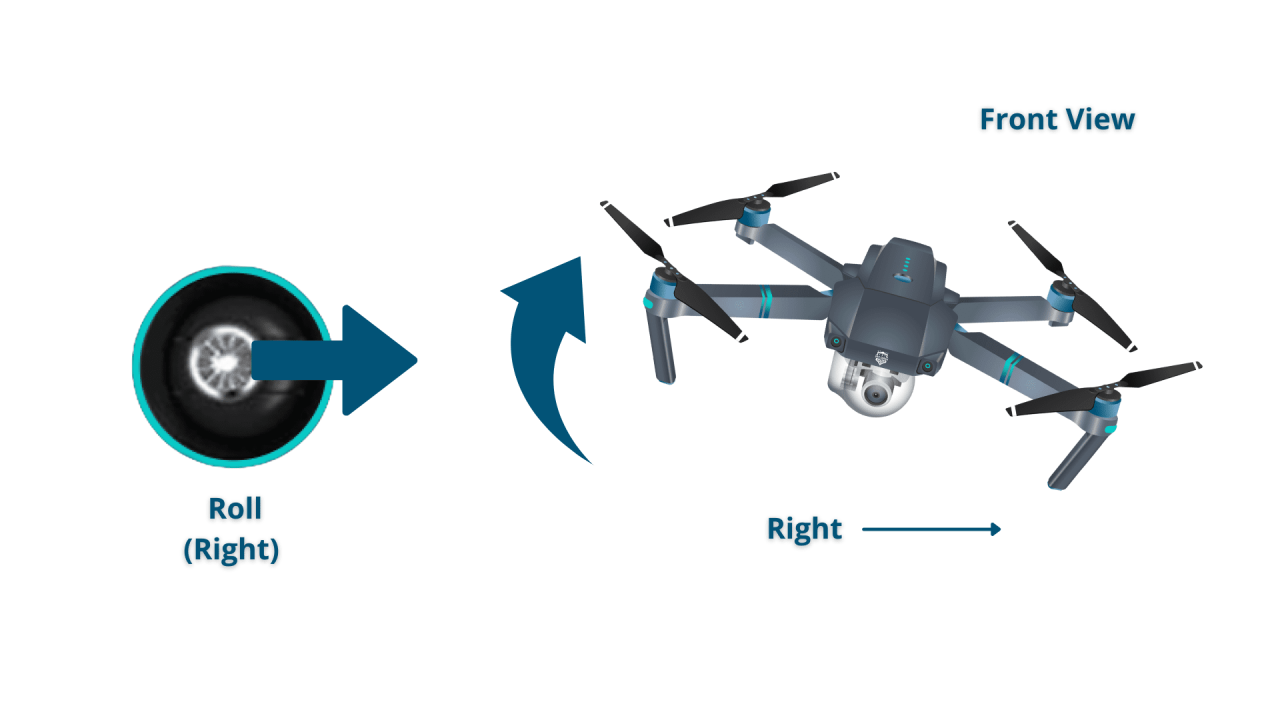
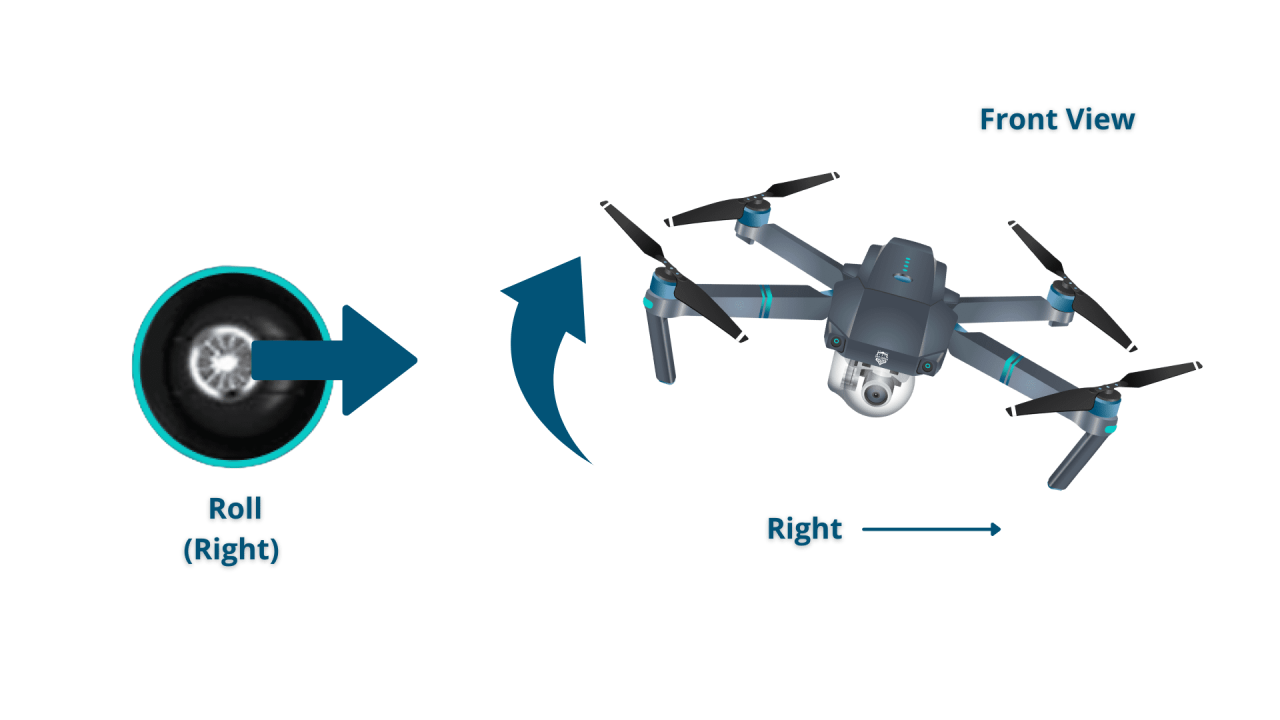
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls and navigation is essential for safe and efficient operation. This involves understanding different controller types, calibration procedures, and flight modes.
Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Various drone controllers exist, ranging from basic to highly sophisticated models. Basic controllers typically feature joysticks for controlling altitude, direction, and camera tilt. More advanced controllers might incorporate additional features like customizable buttons, programmable flight modes, and integrated screens for real-time flight data. Understanding the specific functionalities of your controller is crucial for effective drone operation.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are vital for precise drone positioning and navigation. The calibration process typically involves a series of movements guided by the drone’s software, ensuring the drone accurately understands its orientation and location. Instructions vary depending on the drone model, but generally involve slowly rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern, or performing a specific series of maneuvers indicated on the controller screen.
Tips for Smooth and Precise Drone Maneuvering
Smooth and precise drone maneuvering requires practice and a gentle touch. Avoid abrupt movements, and use small, controlled inputs to adjust the drone’s position and orientation. Mastering techniques like smooth takeoff and landing, precise hovering, and controlled camera movements is essential for capturing high-quality footage.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their differences is crucial for adapting to various situations.
| Flight Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Relies on GPS signals for positioning and stability. | Stable flight, even in windy conditions; precise hovering. | Requires strong GPS signal; may not be suitable for indoor use. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains the drone’s attitude (orientation) relative to its starting position, regardless of GPS signal. | Suitable for indoor or GPS-denied environments; allows for more dynamic movements. | Less stable than GPS mode; requires more pilot skill. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) Mode | Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. | Useful in case of low battery or loss of control. | Requires a strong GPS signal; accuracy may vary depending on conditions. |
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photographs and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial imagery requires understanding the interplay between lighting, camera settings, and drone stability. This section provides guidance on optimizing your drone’s camera for various shooting scenarios.
Factors Influencing Image Quality
Several factors contribute to the quality of your aerial photographs and videos. Optimal lighting conditions are crucial; avoid harsh midday sun which can lead to overexposure and harsh shadows. Proper camera settings, including ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, need to be adjusted based on the lighting conditions and desired effect. Maintaining drone stability is essential for sharp, blur-free images and videos.
Using features like active track or point of interest can further enhance the stability and smoothness of your shots.
Capturing High-Resolution Aerial Photographs
To capture high-resolution aerial photographs, ensure your drone’s camera settings are optimized for the lighting conditions. Use a low ISO value to minimize noise, and adjust the shutter speed to avoid motion blur. Consider using a fast shutter speed for moving subjects, and a slower shutter speed for smoother, more cinematic effects in low-light situations. Experiment with different apertures to control depth of field and create the desired aesthetic.
Achieving Smooth and Steady Video Footage
Smooth and steady video footage requires careful attention to drone stability and camera settings. Utilize features like gimbal stabilization to compensate for minor movements. Employ smooth, controlled movements when panning or tilting the camera. Flying at a consistent speed and altitude contributes to smoother footage. Post-processing techniques like stabilization software can further enhance the smoothness of your videos.
Checklist for Optimizing Drone Camera Settings
A checklist can help ensure consistent, high-quality results. This checklist should adapt to the specific needs of each shot, adjusting parameters such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture based on lighting conditions and subject matter. The checklist should include fields for recording settings used for each shot and noting the results.
Drone Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery care and maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone’s batteries and ensuring safe operation. This includes proper charging, storage, and regular inspection.
Importance of Proper Battery Care and Charging Procedures
Drone batteries are sensitive and require careful handling. Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions precisely. Avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries, as this can damage them and reduce their lifespan. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Routine Drone Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This includes a visual inspection of the airframe, propellers, and other components for any signs of damage or wear. Clean the drone after each flight to remove any dirt or debris. Regularly check the battery health and replace them if necessary. A maintenance log can help track inspections and ensure timely servicing.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Battery Issues
Common battery issues include reduced flight time, inability to charge, and swelling. Reduced flight time can be due to battery age or improper storage. Charging problems may stem from faulty chargers or damaged batteries. Swollen batteries indicate internal damage and should be replaced immediately. Always follow manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting and replacement.
Safe Storage and Transportation of Drone Batteries
Safe storage and transportation of drone batteries are crucial to prevent damage and potential hazards. Follow these procedures:
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
- Use a protective case or bag during transportation.
- Never transport batteries in checked baggage on airplanes.
- Keep batteries away from flammable materials.
- Avoid crushing or puncturing batteries.
Emergency Procedures and Troubleshooting
Knowing how to handle potential malfunctions and emergencies is critical for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for various scenarios and provides troubleshooting tips.
Potential Drone Malfunctions and Responses
Potential malfunctions include loss of GPS signal, low battery warning, motor failure, and communication issues. In case of a loss of GPS signal, attempt to regain signal by moving to an open area with a clear view of the sky. A low battery warning requires immediate attention; initiate a return-to-home procedure. Motor failure necessitates an immediate emergency landing.
Communication issues might require restarting the drone and controller.
Emergency Landing Procedures
Emergency landing procedures vary depending on the scenario. In case of low battery, initiate the return-to-home function immediately. If GPS fails, attempt to manually control the drone to a safe landing zone. In case of motor failure, prioritize a safe, controlled descent, selecting a suitable landing area based on the drone’s altitude and remaining battery life.
Importance of a Backup Plan
Having a backup plan is essential in case of unexpected issues. This could involve having a secondary battery, understanding manual control overrides, or knowing alternative landing zones. Planning for contingencies minimizes risks and ensures safe operation.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch | Regularly check battery charge, store batteries properly |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Move to an open area, recalibrate GPS | Fly in open areas with clear sky view |
| Motor failure | Mechanical failure, software glitch | Emergency landing, contact support | Regular maintenance, software updates |
| Camera malfunction | Software glitch, SD card issue | Restart drone, check SD card | Regular software updates, use high-quality SD cards |
Post-Flight Procedures
Post-flight procedures are just as important as pre-flight checks. They ensure the safe storage of your drone and the preservation of your captured data.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding flying experience.
Post-Flight Drone Inspection and Data Retrieval
After each flight, perform a thorough inspection of your drone for any damage or loose parts. Check the propellers, airframe, and landing gear for signs of wear or damage. Retrieve the captured data from the SD card, ensuring all footage and images are properly saved.
Downloading and Storing Aerial Footage and Images
Download the aerial footage and images to your computer or other storage device. Use a reliable file management system to organize and store your data. Back up your data to prevent loss due to hardware failure or other unforeseen circumstances. Employ appropriate file naming conventions for easy retrieval.
Analyzing Flight Logs, How to operate a drone
Review the flight logs to identify areas for improvement in your flying technique or operational efficiency. Flight logs provide valuable data on flight duration, battery usage, altitude, and other parameters. Analyzing these logs can help refine your skills and enhance your future flights.
Cleaning and Storing the Drone
Clean your drone after each flight to remove any dirt, dust, or debris. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently clean the airframe and other components. Store your drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Keep your drone in a protective case or bag to prevent damage during storage or transportation.
- Clean the drone body and propellers with a soft cloth.
- Inspect for any damage or loose parts.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place.
- Charge the battery to approximately 50% for long-term storage.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical skill, safety awareness, and a keen eye for detail. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the skies responsibly and capture breathtaking aerial content. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and ensuring safe and successful drone flights. Soar responsibly!
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of license or registration do I need to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements. In many places, registration of the drone itself is often mandatory.
How far can I fly my drone?
The maximum distance depends on your drone model, battery life, and local regulations. Most drones have a maximum range, often limited by signal strength and battery capacity. Always stay within visual line of sight unless operating under specific exemptions.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, prepare for an emergency landing, prioritizing safety and avoiding populated areas.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass and GPS?
It’s best practice to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve transported the drone or experienced significant magnetic interference. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.